Amino Acids and Derivatives
Amino acids and their derivatives belong to a compound containing both amino group and carboxyl group. They are presented in both the form of free-state and bound-state in vivo. Free amino acids are distributed in all kinds of animal cells and body fluids with the bound amino acids being the mainly basic components of proteins and peptides.
Natural amino acids act as colorless crystalline materials with relatively high melting points being mostly above 200 ℃. They are usually soluble in water but insoluble in non-polar organic solvents. However, tyrosine and cystine are insoluble in water; proline and hydroxyl proline are soluble in ethanol and ether. All amino acids are soluble in strong acid and alkali solution.
According to the polar characterization of the R group of the side chain of the α-amino acid; those 20 common amino acids that constitute protein can be divided into four groups:
① Amino acids with R group being non-polar; There are 8 kinds in total, wherein five kinds have aliphatic side chains, namely alanine, leucine, isoleucine, valine and proline; two kinds are aromatic amino acids, phenylalanine and tryptophan; one kind belongs to sulfur-containing amino acid, namely methionine; amino acids belonging to this group have lower water solubility than polar R-group amino acid; proline is generally different with α-amino acid, it is formed through the substitution of one hydrogen atom of the amino acid with the side chains of the α- amino acid, belonging actually to imino acid.
② Amino acids with polar but non-charged R group; There are seven kinds in total, namely serine, threonine and tyrosine with R group having hydroxy group; cysteine with R group having a mercapto group of cysteine; glutamine and asparagine with R-group containing amide group, another amino acid is glycine ; glycine molecule has no R group, but having certain polarity, and thus being classified into this group; the side chains in this group of amino acid contain unassociated polar groups and can form hydrogen bonds with water, and is easily soluble in water.
③Amino acids with R group being positively charged amino acids. There are three kinds in total, namely, lysine, arginine, and histidine; they carry positive charge at pH7.0 and are also known as alkaline amino acids.
④Amino acids with R group being negatively charged. There are two kinds in total, namely glutamate and aspartate; at pH7.0, the molecules are negatively charged, also known as acidic amino acids. The formula, abbreviations symbols and related constants of 20 kinds of amino acid structures can be seen from the table. In addition to the 20 common amino acids mentioned above, there are also diiodotyrosine, thyroxine, hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine existing in certain proteins. In addition to amino acids involved in protein composition, it has been also found of more than 200 kinds of other kinds amino acids in a variety of tissues and cells; these amino acids are mostly derivatives of those α- amino acid composition of proteins.
However, there are some β-, γ- or δ- amino acids and some amino acids belong to D-type amino acids such as [beta]-alanine, [gamma]-aminobutyric acid and the phenylalanine contained in the antibiotics gramicidin-S, the D-alanine and D-glutamate contained in Gram-positive bacteria cell wall. Some non-protein amino acids can act as metabolically important precursors or intermediates, wherein β-alanine is the precursors of vitamin pantothenic acid; ornithine, and citrulline are the precursors in the synthesis of arginine; [gamma]-aminobutyric acid is the chemical neurotransmitter. Plants contain a large amount of non-protein amino acids, belonging to plant secondary substances, such as theanine, canavanine, djenkolic acid, β- Cyanoalanine and so on.
In addition to 20 kinds of amino acids found in the body and animal protein products, it has been found of nearly 200 kinds of other kinds of amino acids in nature. Most of them have been discovered in the plant kingdom and have complex molecular structures with no relation with the protein metabolism. There have been less that have been seen in the animal kingdom with some of them being originated from the chemical modification of certain incorporated amino acids in the specific proteins, for example, the proline and lysine contained in collagen protein are often partially subject to re-hydroxylation of hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine; Another example is that there are often a small amount of lysine and histidine contained in actin and myosin protein containing hypermethylated εN methyl-lysine and 3N-histidine; it has been also found in the histone protein that the ∈ amino group contained in lysine is acetylated and the OH group in the serine is phosphorylated; thyroglobulin contains iodinated tyrosine and thyronine iodide; The heavy chain of τ myosin and the N-terminal of certain proteins contain pyroglutamate formed by glutamine; there also exists the cystine constituting of two cysteine molecules in the general protein.
Click on the specific product, view the latest prices of the products, information, serving information
- Structure:
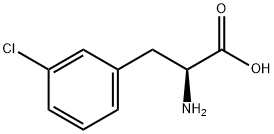
- Chemical Name:
- L-3-Chlorophenylalanine
- CAS:
- 80126-51-8
- MF:
- C9H10ClNO2
- Structure:
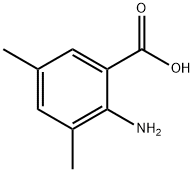
- Chemical Name:
- 2-Amino-3,5-dimethylbenzoic acid
- CAS:
- 14438-32-5
- MF:
- C9H11NO2
- Structure:
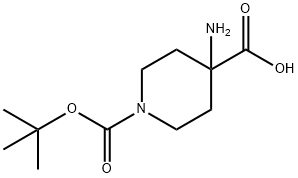
- Chemical Name:
- 4-AMINO-1-BOC-PIPERIDINE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID
- CAS:
- 183673-71-4
- MF:
- C11H20N2O4
- Structure:
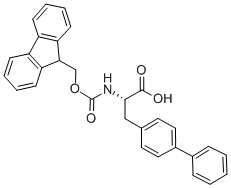
- Chemical Name:
- FMOC-L-4,4'-BIPHENYLALANINE
- CAS:
- 199110-64-0
- MF:
- C30H25NO4
- Structure:
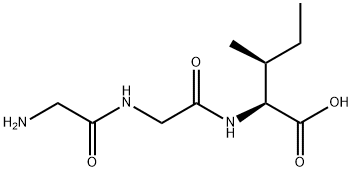
- Chemical Name:
- Glycylglycyl-L-isoleucine
- CAS:
- 69242-40-6
- MF:
- C10H19N3O4
- Structure:
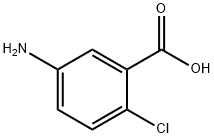
- Chemical Name:
- 5-Amino-2-chlorobenzoic acid
- CAS:
- 89-54-3
- MF:
- C7H6ClNO2
- Structure:
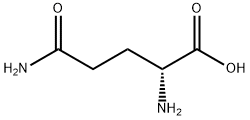
- Chemical Name:
- D-Glutamine
- CAS:
- 5959-95-5
- MF:
- C5H10N2O3
- Structure:
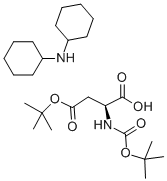
- Chemical Name:
- 4-tert-Butyl N-[(tert-butoxy)carbonyl]-L-aspartate dicyclohexylamine salt
- CAS:
- 1913-12-8
- MF:
- C13H23NO6.C12H23N
- Structure:
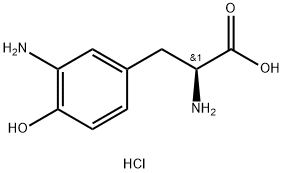
- Chemical Name:
- 3-AMINO-TYROSINE-2 HCL
- CAS:
- 23279-22-3
- MF:
- C9H13ClN2O3
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- N-Fmoc-L-threonol
- CAS:
- 176380-53-3
- MF:
- C19H21NO4
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- Methyl D-valinate hydrochloride
- CAS:
- 7146-15-8
- MF:
- C6H14ClNO2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- D-Tryptophanol
- CAS:
- 52485-52-6
- MF:
- C11H14N2O
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- N-Cbz-D-Leucine
- CAS:
- 28862-79-5
- MF:
- C14H19NO4
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- N-BOC-L-Prolinal
- CAS:
- 69610-41-9
- MF:
- C10H17NO3
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- N-BOC-cis-4-fluoro-L-proline
- CAS:
- 203866-13-1
- MF:
- C10H16FNO4
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- (L-3-TRANS-CARBOXYOXIRANE-2-CARBONYL)-L-LEUCYLAGMATINE HEMIHYDRATE
- CAS:
- 66701-25-5
- MF:
- C15H27N5O5
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- Boc-Ser(tBu)-OH
- CAS:
- 13734-38-8
- MF:
- C12H23NO5
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- L(+)-Monosodium glutamate monohydrate
- CAS:
- 6106-04-3
- MF:
- C5H12NNaO5
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- 3-Amino-4-chlorobenzoic acid
- CAS:
- 2840-28-0
- MF:
- C7H6ClNO2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- 6-AMINO-2-NAPHTHOIC ACID
- CAS:
- 116668-47-4
- MF:
- C11H9NO2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- Dimethyl L-aspartate hydrochloride
- CAS:
- 32213-95-9
- MF:
- C6H12ClNO4
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- L-tert-Leucine methyl ester hydrochloride
- CAS:
- 63038-27-7
- MF:
- C7H16ClNO2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- DL-beta-(3-Bromophenyl)alanine
- CAS:
- 117391-50-1
- MF:
- C9H10BrNO2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- N-BOC-1,6-DIAMINO-HEXANE HYDROCHLORIDE
- CAS:
- 65915-94-8
- MF:
- C11H25ClN2O2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- Glycylglycine
- CAS:
- 556-50-3
- MF:
- C4H8N2O3
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- 3-FLUORO-D-PHENYLALANINE
- CAS:
- 2629-54-1
- MF:
- C9H10FNO2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- KYNURENIC ACID
- CAS:
- 492-27-3
- MF:
- C10H7NO3
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- DL-LEUCYL-GLYCYL-GLYCINE
- CAS:
- 4337-37-5
- MF:
- C10H19N3O4
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- N-Carbobenzyloxyglycine
- CAS:
- 1138-80-3
- MF:
- C10H11NO4
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- D-Leucine methyl ester hydrochloride
- CAS:
- 5845-53-4
- MF:
- C7H16ClNO2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- Fmoc-3-chloro-D-phenylalanine
- CAS:
- 205526-23-4
- MF:
- C24H20ClNO4
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- (R)-3-AMINO-3-(4-CHLORO-PHENYL)-PROPIONIC ACID
- CAS:
- 131690-61-4
- MF:
- C9H10ClNO2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- Fmoc-Met-OH
- CAS:
- 112883-40-6
- MF:
- C20H21NO4S
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- H-D-DAP-OH HCL
- CAS:
- 6018-56-0
- MF:
- C3H9ClN2O2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- L(+)-2-Aminobutyric acid
- CAS:
- 1492-24-6
- MF:
- C4H9NO2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- 4-Fluorophenylglycine
- CAS:
- 7292-73-1
- MF:
- C8H8FNO2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- D-1-Naphthylalanine
- CAS:
- 78306-92-0
- MF:
- C13H13NO2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- H-MEVAL-OH HCL
- CAS:
- 2480-23-1
- MF:
- C6H13NO2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- 6-FLUORO-DL-TRYPTOPHAN
- CAS:
- 7730-20-3
- MF:
- C11H11FN2O2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- Fmoc-3-chloro-L-phenylalanine
- CAS:
- 198560-44-0
- MF:
- C24H20ClNO4
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- Fmoc-D-phenylalanine
- CAS:
- 86123-10-6
- MF:
- C24H21NO4
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- N-Acetyl-DL-tryptophan
- CAS:
- 87-32-1
- MF:
- C13H14N2O3
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- BOC-L-3-THIENYLALANINE DCHA SALT
- CAS:
- 83825-42-7
- MF:
- C12H17NO4S
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- Boc-Arg(Tos)-OH
- CAS:
- 13836-37-8
- MF:
- C18H28N4O6S
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- (1S,2R)-2-Amino-1,2-diphenylethanol
- CAS:
- 23364-44-5
- MF:
- C14H15NO
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- L(+)-Ornithine hydrochloride
- CAS:
- 3184-13-2
- MF:
- C5H13ClN2O2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- 3-Amino-2-naphthoic acid
- CAS:
- 5959-52-4
- MF:
- C11H9NO2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- L-Tyrosinol hydrochloride
- CAS:
- 87745-27-5
- MF:
- C9H14ClNO2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- H-TYR-NH2 HCL
- CAS:
- 4985-46-0
- MF:
- C9H12N2O2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- Methyl 1-aminocyclopropanecarboxylate hydrochloride
- CAS:
- 72784-42-0
- MF:
- C5H10ClNO2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- O-PHOSPHO-L-TYROSINE
- CAS:
- 21820-51-9
- MF:
- C9H12NO6P
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- (R)-3-AMINO-3-(3-CHLORO-PHENYL)-PROPIONIC ACID
- CAS:
- 262429-49-2
- MF:
- C9H10ClNO2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- Fmoc-O-benzyl-L-serine
- CAS:
- 83792-48-7
- MF:
- C25H23NO5
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- N-CARBOBENZOXY-L-SERINE BETA-LACTONE
- CAS:
- 26054-60-4
- MF:
- C11H11NO4
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- BOC-(S)-3-AMINO-4-(3-CYANO-PHENYL)-BUTYRIC ACID
- CAS:
- 270065-86-6
- MF:
- C16H20N2O4
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- FMOC-CYS(MMT)-OH
- CAS:
- 177582-21-7
- MF:
- C38H33NO5S
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- FMOC-LYS(BOC)(ME)-OH
- CAS:
- 951695-85-5
- MF:
- C27H34N2O6
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- 3-(2-Quinolyl)-DL-alanine
- CAS:
- 123761-12-6
- MF:
- C12H12N2O2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- GLYCYLGLYCINE METHYL ESTER HYDROCHLORIDE
- CAS:
- 2776-60-5
- MF:
- C5H11ClN2O3
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- N-Boc-cis-4-Fmoc-Amino-L-proline
- CAS:
- 174148-03-9
- MF:
- C25H28N2O6
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- Z-TRANS-4-HYDROXY-L-PROLINOL
- CAS:
- 95687-41-5
- MF:
- C13H17NO4
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- Boc-N-beta-Trityl-L-asparagine
- CAS:
- 132388-68-2
- MF:
- C28H30N2O5
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- (R)-3-AMINO-4-(3-BENZOTHIENYL)BUTANOIC ACID HYDROCHLORIDE
- CAS:
- 269398-95-0
- MF:
- C12H13NO2S
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- N6-Trifluoroacetyl-L-lysyl-L-proline
- CAS:
- 103300-89-6
- MF:
- C13H20F3N3O4
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- BOC-(R)-3-AMINO-4-(2-FLUORO-PHENYL)-BUTYRIC ACID
- CAS:
- 218608-98-1
- MF:
- C15H20FNO4
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- BOC-ARG-OH
- CAS:
- 13726-76-6
- MF:
- C11H22N4O4
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- 1-METHYL-DL-TRYPTOPHAN
- CAS:
- 26988-72-7
- MF:
- C12H14N2O2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- L-Histidine hydrochloride
- CAS:
- 1007-42-7
- MF:
- C6H10ClN3O2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- H-LEU-D-LEU-OH
- CAS:
- 17665-02-0
- MF:
- C12H24N2O3
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- L-BETA-HOMOSERINE
- CAS:
- 16504-56-6
- MF:
- C4H9NO3
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- 4-FLUORO-DL-GLUTAMIC ACID
- CAS:
- 2708-77-2
- MF:
- C5H8FNO4
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- BOC-THR(ME)-OH
- CAS:
- 48068-25-3
- MF:
- C10H19NO5
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- H-D-ARG(NO2)-OME HCL
- CAS:
- 50912-92-0
- MF:
- C7H16ClN5O4
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- H-PHE-PNA HCL
- CAS:
- 2360-97-6
- MF:
- C15H15N3O3
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- 3,4-DEHYDRO-DL-PROLINE
- CAS:
- 3395-35-5
- MF:
- C5H7NO2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- AMINO-(TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-YL)-ACETIC ACID
- CAS:
- 53284-84-7
- MF:
- C7H13NO3
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- FMOC-GLY-OPFP
- CAS:
- 86060-85-7
- MF:
- C23H14F5NO4
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- trans-1-Benzoyl-4-phenyl-L-proline
- CAS:
- 120851-71-0
- MF:
- C18H17NO3
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- BOC-D-STYRYLALANINE DCHA SALT
- CAS:
- 261380-19-2
- MF:
- C16H21NO4
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- Glycine tert butyl ester hydrochloride
- CAS:
- 27532-96-3
- MF:
- C6H14ClNO2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- Poly(L-lysine hydrobromide)
- CAS:
- 25988-63-0
- MF:
- C6H14N2O2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- L-Tyrosine Ethyl Ester Hydrochloride
- CAS:
- 4089-07-0
- MF:
- C11H16ClNO3
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- S-Cbz-L-cysteine
- CAS:
- 1625-72-5
- MF:
- C11H13NO4S
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- 1,2-Bis(bromomethyl)benzene
- CAS:
- 91-13-4
- MF:
- C8H8Br2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- (R)-N-Boc-(3-Pyridyl)alanine
- CAS:
- 98266-33-2
- MF:
- C13H18N2O4
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- BOC-GAMMA-ABU-OH
- CAS:
- 57294-38-9
- MF:
- C9H17NO4
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- BETA-(2-THIENYL)-DL-ALANINE
- CAS:
- 2021-58-1
- MF:
- C7H9NO2S
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- 6-METHYL-DL-TRYPTOPHAN
- CAS:
- 2280-85-5
- MF:
- C12H14N2O2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- (-)-ALPHA-[1-(DIBUTYLAMINO)ETHYL]BENZYL ALCOHOL
- CAS:
- 114389-70-7
- MF:
- C17H29NO
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- BOC-D-PRO-OME
- CAS:
- 73323-65-6
- MF:
- C11H19NO4
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- BZ-GLU-OH
- CAS:
- 6094-36-6
- MF:
- C12H13NO5
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- (2R,4R)-N-Boc-4-hydroxypyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid
- CAS:
- 135042-12-5
- MF:
- C10H17NO5
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- Aceglutamide
- CAS:
- 2490-97-3
- MF:
- C7H12N2O4
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- BOC-D-PHE(4-NHBOC)-OH
- CAS:
- 214750-77-3
- MF:
- C29H30N2O6
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- FMOC-2-NAL-OH
- CAS:
- 112883-43-9
- MF:
- C28H23NO4
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- L-4-Iodophenylalanine
- CAS:
- 24250-85-9
- MF:
- C9H10INO2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- (S)-3-AMINO-4-(4-FLUOROPHENYL)BUTANOIC ACID HYDROCHLORIDE
- CAS:
- 270596-53-7
- MF:
- C10H12FNO2
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- BOC-N-ME-SER-OH
- CAS:
- 101772-29-6
- MF:
- C9H17NO5
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- BOC-CYS(4-MEOBZL)-OH
- CAS:
- 18942-46-6
- MF:
- C16H23NO5S
- Structure:
- Chemical Name:
- FMOC-D-DAP(BOC)-OH
- CAS:
- 198544-42-2
- MF:
- C23H26N2O6